Creating Empathy Maps: Understanding Your Users to Build Better Products

In the high-stakes world of product management, understanding your customers profoundly is paramount to developing products that truly meet their needs. One powerful method to achieve this is by creating Empathy Maps. Empathy maps help teams uncover insights about users' experiences, and align better with their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. In this post, we'll delve into how to construct effective empathy maps, share best practices, and illustrate their significance through real-world success stories.
What is an Empathy Map?
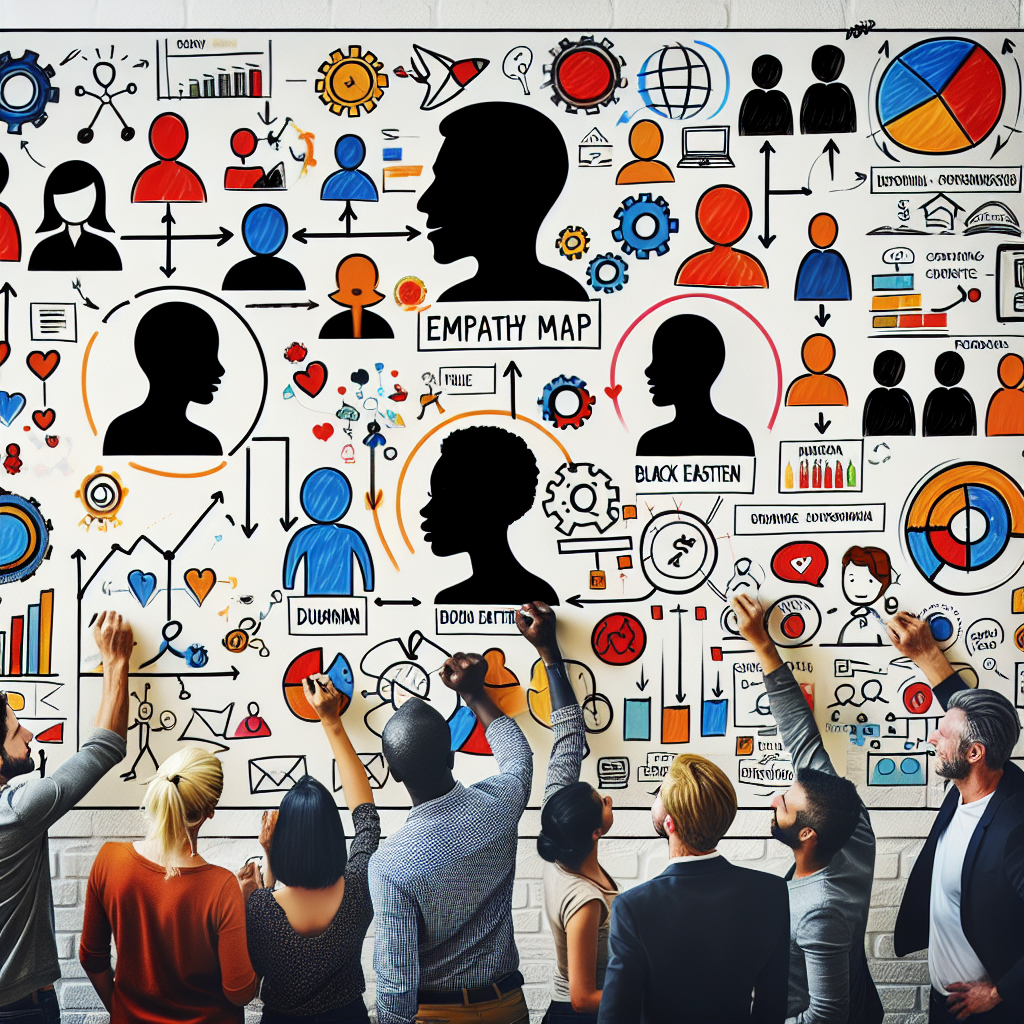
An empathy map is a visual tool that represents the user's feelings, thoughts, and behaviors. Typically divided into four quadrants—Says, Thinks, Does, and Feels—it's designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the user from their perspective. This holistic approach helps product managers and their teams craft solutions that are deeply rooted in user empathy.
Steps to Create an Empathy Map
1. Define the Purpose and Scope
First, determine the purpose of your empathy mapping exercise. Identify the specific user segment you want to explore and understand their interaction with your product.
2. Gather User Data
Collect qualitative data through user interviews, surveys, observational studies, and customer feedback. Your goal is to capture authentic user experiences and insights.
3. Identify the User Persona
Create a user persona that embodies the characteristics of your target user group. This persona will be the focal point of your empathy map.
4. Construct the Empathy Map
Divide a large sheet or digital canvas into four quadrants: Says, Thinks, Does, and Feels. Optionally, you can add an additional two quadrants—Pains and Gains—to capture struggles and successes.
- Says: Direct quotes or paraphrased user statements.
- Thinks:
- Does: Actions and behavior patterns observed.
- Feels: Emotional states and sentiments.
5. Populate the Empathy Map
Using the data gathered, populate each quadrant with relevant insights. Encourage team members to contribute and discuss observations for a richer understanding.
6. Analyze and Synthesize Insights
Analyze the empathy map to identify patterns, themes, and discrepancies. Use these insights to inform product decisions, design improvements, and user experience enhancements.
Best Practices for Empathy Mapping
1. Involve Cross-Functional Teams
Engage team members from various functions like design, development, marketing, and customer support in the empathy mapping process. Diverse perspectives lead to a more comprehensive understanding of user needs.
2. Prioritize User Authenticity
Ensure that the insights on your empathy map genuinely reflect user experiences. Avoid assumptions or biases that might skew the data.
3. Keep It Updated
Revisit and revise the empathy map regularly as you gather more data and your understanding of the user evolves. An up-to-date map ensures that product decisions remain aligned with user needs.
4. Use Empathy Maps as Discussion Tools
Leverage empathy maps during team meetings and decision-making processes. They serve as powerful reminders of the user perspective and foster user-centric thinking within the team.
Success Stories and Lessons Learned
Case Study: Healthcare App Development
A healthcare startup employed empathy maps to understand the daily challenges of chronic disease patients. They discovered that patients felt overwhelmed by managing complex medication schedules. By simplifying their app's user interface and incorporating medication reminders, the team significantly improved the app's usability and patient adherence to treatment plans.
Case Study: E-commerce User Experience
An e-commerce platform used empathy maps to explore why users abandoned their shopping carts. They learned that users were frustrated by the lengthy checkout process and unexpected shipping costs. Streamlining the checkout flow and displaying shipping fees earlier resulted in a 30% increase in completed purchases.
Pitfall: Overlooking Emotional Data
A SaaS company initially ignored the emotional aspect of their empathy maps, focusing solely on functional insights. This approach led to several missed opportunities to address user frustrations. Incorporating emotional data later revealed key areas for enhancing user satisfaction which subsequently improved customer retention rates.
Conclusion
Empathy maps are essential tools for product managers to gain profound insights into user needs and experiences. By following best practices and incorporating real-world learnings, you can leverage empathy maps to build user-centric products that resonate with your audience. Have you used empathy maps in your product management processes? Share your experiences and tips in the comments below!